Exif created by JPEGTweaker
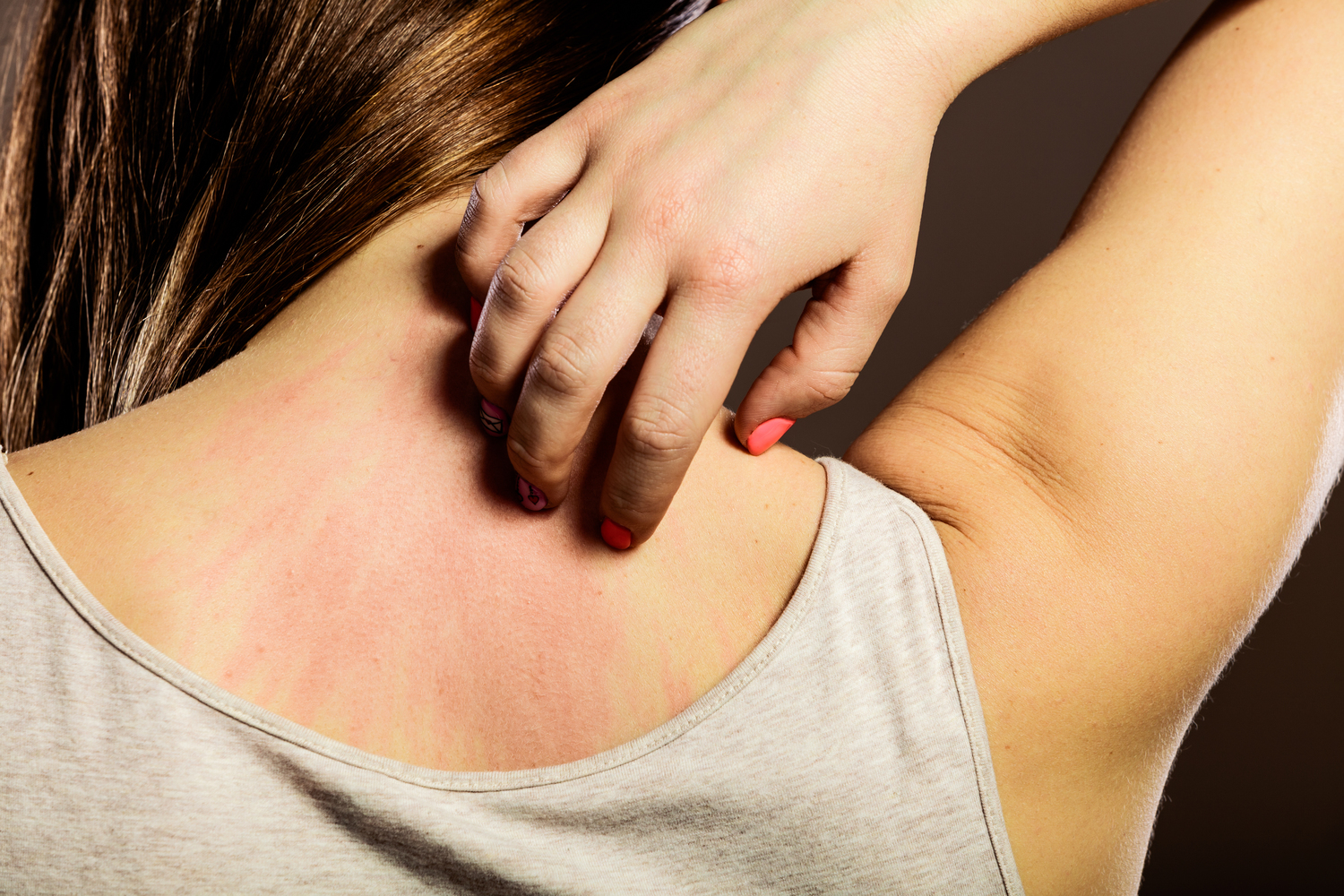
Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as Eczema, is a common skin condition marked by itchy and inflamed patches of skin.
The types of eczema include:
Contact dermatitis
Usually caused by contact with irritants, causing burning, itching, and redness.
Dyshidrotic dermatitis
This affects the fingers, palms of the hands, and soles of the feet, causing itchy, scaly patches of skin that flake or become red, cracked, and painful.
Nummular dermatitis
This causes round, dry patches of skin during the winter, usually affecting the legs.
Seborrheic dermatitis
This causes itchy, red, scaly rashes, especially on the scalp, on the sides of the nose, on the eyebrows, on the eyelids, and behind the ears.
Symptoms
The main symptom is itchy, dry, rough, flakey, inflamed, and irritated skin which flares up, subsides, and then flares up again. Eczema occurs anywhere on the body, but usually affects the arms, inner elbows, backs of the knees, or head. It isn’t contagious, & in some cases, loses its severity with age.
Other symptoms include:
- intense itching
- red or brownish-gray patches
- small, raised bumps that ooze when scratched
- crusty patches of dried yellowish ooze
- thickened, scaly skin
Causes
Eczema is triggered by an overactive immune system responding aggressively on exposure to irritants. In eczema, the immune system loses the ability to tell the difference between proteins that are part of the human body & the proteins of invaders, such as bacteria or viruses, which causes inflammation.
Common triggers of eczema are:
- chemicals in cleaners & detergents
- rough scratchy material
- synthetic fabric
- raised body temperature
- sweating
- temperature changes
- drop in humidity
- stress
Treatment
Your dermatologist, primary care doctor or allergist can help you identify the treatment for eczema that works for you.
Some options are:
Medications
- Oral over-the-counter antihistamines may relieve itching. They block histamine, which trigger allergic reactions.
- Cortisone creams and ointments can relieve itching and scaling.
- Immunosuppressants help with flare-ups by preventing the immune system from overreacting.
- Therapies
Light therapy uses ultraviolet light or sunlamps to prevent immune system responses that trigger eczema flare-ups. A series of treatments can help reduce eczema, prevent bacterial skin infections or even clear it up.
Lifestyle changes
Stress can trigger or exacerbate symptoms of eczema. Ways to reduce stress:
- deep breathing exercises
- practicing yoga
- meditating
- relaxing music
- a good night’s sleep
A cold compress can also help alleviate itching, as well as soaking for 15 to 20 minutes in a lukewarm bath.








